If a person has a fungus on their leg, it is important to start treatment in a timely and appropriate manner. This is because a fungal disease of the skin of the feet is contagious, and if you do not start fighting the disease immediately, all members of the patient's family are at risk of infection. The treatment is prescribed by a doctor, depending on the type of pathology, the degree of damage to the skin and the general condition of the person.

Causes of the appearance of the fungus on the legs
Once in the skin of the feet, the fungus does not always cause mycoses, and for the first symptoms to appear, negative factors must act on the human body. The following negative causes affect the development of mycosis:

- weakening of the body's immune system;
- use of heavy and toxic drugs;
- non-compliance with foot and toe hygiene rules;
- the presence of cracks, wounds and abrasions on the toes and feet through which fungal spores can enter the body.
The site of fungal infection is the wet floors of swimming pools, baths and showers in the gyms.
Fungal infection enters the body through contact-household contact with an adult or child with a carrier or objects inhabited by fungal spores. Leg fungi can often be picked up in public places - locker rooms, showers, pools, beaches. The disease can also pass if you wear someone else’s shoes that are inhabited by pathogenic spores. Failure to follow basic hygiene rules can lead to undesirable consequences that cause fungal pathologies of the feet and nails. The carrier may not always be able to find out in time that the foot fungus is present, as the symptoms only occur when combined with adverse conditions. But such a person is still contagious and it is dangerous for loved ones who are also at risk of infectious infection.
Symptoms and types
There are the following forms of leg mycosis:
- quasi;
- dehydrotic;
- intertriginal;
- onychomycosis;
- candidate.
Laphám
The initial symptoms of this form of fungus are found on only one leg, however, as the pathology progresses, a manifestation is observed on the other leg. The disease appears to be a skin defect on which inflammation develops and is covered with exfoliation. Psoriasis of the foot is not always characterized by itching and discomfort, so for many, the disease goes unnoticed and is impossible to detect without a laboratory test.
If the foot fungus does not heal in time, the infectious lesion passes into the tibia, it will be much more difficult to treat the problem. The fungus can also be localized on calves, however, these complications are rare.
Dyshydrotic
The first signs of the fungus on the feet of this shape are characterized by the formation of bubbles in the arch of the foot, which gradually grow and reach a diameter of 10 mm. After the rash opens, it hurts and is eroded. The sites of damage are painful, there are cases of bacterial inflammation. Once the skin in the diseased areas heals, the disease progresses to squamous cell form. In the dehydrotic version, the skin of the two legs is rarely affected, if treatment is not started in time, a neglected form develops in which the stages of remission alternate with exacerbation.
intertrigo
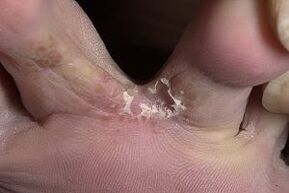
Intertriginal or interdigital fungus is the most common form of skin disease.
This type of leg fungus is the most common. The skin between the 4th and 5th toes is most commonly affected. The disease manifests itself in the formation of dead, scaly areas that peel off the normal layer of the epidermis.
If you do not provide help in time, the flaky areas will start to get wet and the patient will feel pain and itching. In addition, wounds and erosions occur in the affected areas, which are difficult to eradicate.
If you do nothing and ignore the symptoms, the disease develops into a chronic form that tends to relapse frequently.
Onychomycosis
The disease is characterized by localization of the fungus on the nails and toes. First, the fungus of the nail manifests as an injury to the free edge of the nail, on which spots and streaks of a yellowish tinge are formed. There are the following types of fungi on nails and toes:
- Hypertrophic. The nail plate thickens, turns yellow, is easily destroyed. Under the affected foci, the affected skin of the finger is visible.
- atrophic. The nail thins, is quickly destroyed, and the underlying dermis keratinizes.
- Onychomycosis caused by fungi. The nail plate becomes thinner and turns black, brown, yellowish or green. The disease is a complication of the previous 2 types of pathology.
candida
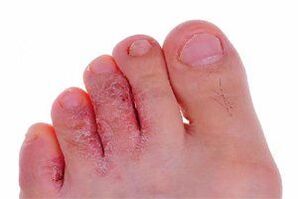
The fungus infects the skin between the toes, leading to bacterial infection without proper treatment.
This type of disease is caused by yeast-like pathogenic fungi called Candida. Inflammatory foci are often located on the skin between 3 and 4 or 4 and 5 fingers. At these sites, the tissues become inflamed, edema develops, and often a bacterial complication also joins.
The Candida fungus is a microorganism that infects human mucous membranes and the outer skin. Normally, Candida is present in limited amounts in the human body. However, as immunity declines, it may show increased activity, causing discomfort to the patient.
If the fungus is not removed in the initial stage, pustules, cracks and erosion are formed which are difficult to get rid of even with the help of strong medicines.
Diagnostic methods
In order for the treatment of fungus on the feet to be effective, it is important to determine the pathogen and make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, you may want to see a doctor who will often be able to diagnose the pathology after the first visual examination. If the skin pathology appears suspicious or does not resolve with treatment for a long time, blood and urine tests should be performed, as well as additional diagnostic testing to help determine the type and susceptibility of the pathogens. antifungal agents. To do this, a piece of skin is removed from the injured area and examined under a microscope. To check for malignant cells in the tissues, samples are taken from the damaged areas for biopsy.
What to treat?

There are a number of fungal diseases that are tested in order to differentiate them and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A healthcare professional should undergo advice and diagnostic measures to cure the foot fungus and prevent recurrence. If the diagnosis is made correctly, you can start therapy with systemic and topical medications.
It is effective in the initial phase of treatment and can then be managed during treatment with external devices in the form of creams, ointments and sprays. The fungus can also be treated with home remedies. If the disease has affected the deep layers of the dermis and the nail plates, it is recommended to use a systemic drug to control the fungus.
Treatment with folk remedies is effective only in combination with the use of drugs, otherwise the disease threatens to develop dangerous complications.
Drug treatment
An effective and efficient medicine must be prescribed by a doctor. If you self-medicate and ignore the advice of a professional, you can cause serious complications that the most effective medicine will not be able to cope with right away.
Therapy with folk remedies
Treatment of foot fungus with folk remedies at home should be agreed with your doctor. It is important to know that strong medicines are used to treat foot and nail fungi, folk remedies are allowed as adjuvant therapy because it is not effective to fight the disease on your own at home. There are various recipes that use herbs with antimicrobial, disinfectant and wound healing properties. Folk remedies for fungi are affordable and inexpensive, but which home method is better to use and what prescription is appropriate for a particular case, you should consult a doctor. The best recipes are:
- Decoction with chamomile, plantain and succession herbs. Mix the ingredients, 1 tbsp each. l. Pour everything into a pan and pour 1 liter of hot water, bring to a boil and let it cook for up to 10 minutes. After broth, filter and wash affected hands, feet and other body parts before going to bed. The essence of the procedure is to perform it regularly, then this method will be effective and will help to treat the fungus faster.
- Infusion of onions and St. John's wort. Peel the onion and cut into 4 slices. St. John's wort should be dried. Pour the onion and 50 g of St. John's wort with 2. 5 liters of boiling water. Pack the container with raw materials and let stand for a day. In the evening, apply an compress from the infusion to the affected areas.
Prevention
The best preventive measure in the fight against the fungus that can prevent the disease is to strengthen the protective properties of the body. This method is inexpensive but the most effective and efficient. Medications and alternative treatments should be discussed with your doctor, and any self-medication can cause dangerous complications that can then be much more difficult and time-consuming to treat.






























